Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kakuta, Ryunosuke*; Takamura, Masato*; Xu, P. G.; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Takanashi, Takaoki*; Otake, Yoshie*; Kurihara, Ryo*; Takahashi, Susumu*; Suzuki, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Sano, Asami
no journal, ,
Hydrogen is one of the key components of the Earth. The neutron scattering which has an advantage in detecting the hydrogen hence can become a powerful tool in the Earth science. The pressure and temperature increase with depth and approach around 14 GPa and 1400 C at the base of the upper mantle of 410 km. The difficulty of the neutron scattering experiment under such extreme conditions comes from the trade-off between pressure and the sample volume. The beamline PLANET in MLF, J-PARC aims to provide platform of neutron powder diffraction under high pressure. This is the first neutron beamline with a multi-anvil press. The large volume press that can compress the sample to over 12 GPa with the volume of approximately 50 mm
C at the base of the upper mantle of 410 km. The difficulty of the neutron scattering experiment under such extreme conditions comes from the trade-off between pressure and the sample volume. The beamline PLANET in MLF, J-PARC aims to provide platform of neutron powder diffraction under high pressure. This is the first neutron beamline with a multi-anvil press. The large volume press that can compress the sample to over 12 GPa with the volume of approximately 50 mm allows us to measure the powder diffraction in-situ under upper mantle conditions. The crystallographic information of minerals including hydrogen poCsition provides fundamental understanding of its properties.
allows us to measure the powder diffraction in-situ under upper mantle conditions. The crystallographic information of minerals including hydrogen poCsition provides fundamental understanding of its properties.
Oba, Yojiro
no journal, ,
Neutron scattering is widely used to characterize microstructures in steels, while neutron transmission spectroscopy is also useful for the microstructural characterization. Recent development of pulsed neutron facilities allows combined use of neutron scattering and neutron transmission. This increases flexibility in experiments and is suitable to the total characterization of complex microstructures in steels. Possibilities of advanced experiments using the combination of neutron scattering and transmission are discussed.
Oi, Motoki; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto
no journal, ,
J-PARC neutron source facility is 1MW pulsed spallation neutron source in Japan. There are three liquid hydrogen moderators, one is for high intensity, the others are for short pulse neutron beam. In order to make short pulsed neutron beam, neutron absorber called decoupler is attached around the moderators. Characteristics of the decoupler is described by the neutron cut-off energy (Ed). In J-PARC, Ed of 1eV is realized by the Ag-In-Cd decoupler at the 1MW spallation neutron source. Due to the radiation damage and burn-up of the decoupler material, we have to replace these moderator and reflector assembly in near future. For the second moderator and reflector assembly, we developed a Au-In-Cd alloy as a low activation material. Ed of Au-In-Cd alloy is 1eV. Activation of the Au-In-Cd is much lower than that of Ag alloy. We manufactured the Au-In-Cd alloy and processed the alloy by ourselves. Finally, it was installed into the moderator and reflector assembly.
Su, Y. H.; Gong, W.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Masuda, Shiho; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakai, Eiichi; Nemoto, Hideyuki; Ikeda, Yujiro; Haga, Katsuhiro
no journal, ,
In the Materials and Life science experimental Facility at J-PARC, pulsed neutrons are provided by a mercury target via spallation reactions. During the target vessel replacement, gaseous spallation products are released from the mercury circulation system to outside. The release of radioactive gases needs to be reduced to a negligibly small level by a purging process in advance of replacement. The radioactivity of noble gases decreased by the purging process while that of tritium was almost unchanged. It is considered that most of tritium produced in mercury is accumulated in the vessel made of stainless-steel and is gradually desorbed during the purging and the vessel replacement. However, there have been no effective data associated with tritium behavior in an environment of mercury spallation target. Then, authors decided to develop an experimental system to understand these phenomena quantitatively and to discuss procedures to minimize tritium release during the vessel replacement. As a first step, we start experiments using deuterium before using tritium. Accumulation and release behaviors of deuterium to stainless-steel are examined under vacuum, controlled humidity and mercury coexistence conditions. Results are expected to be used to establish safer the target vessel replacement.
Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao
no journal, ,
Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.*; Yamashita, Takayuki; Morooka, Satoshi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Aizawa, Kazuya
no journal, ,
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Takuro
no journal, ,
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko; Murai, Naoki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Wakai, Daisuke*
no journal, ,
AMATERAS is one of the first generation disk-chopper spectrometers with pulse-shaping operation as with CNCS at SNS and LET at ISIS, and it is designed to carry out inelastic and quasielastic neutron scattering experiments in the range from cold to sub-thermal neutron energy with high intensity and fine and flexible energy resolution. AMATERAS started its operation from May 2009 and was opened for the user program from December 2009. Up to now, experiments of more than 160 proposals have been carried out, which resulted in more than 50 papers, 15 theses and 11 press releases. Also, AMATERAS took part in the social activities of MLF, for example, hands-on-experiments at AONSA Neutron Schools. Along with performing a user program, we are continually maintaining and improving the performance of the spectrometer. In this presentation, we will show the over view and current status of AMATERAS and recent scientific highlights obtained from experiments by using AMATERAS.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Mukai, Tomohisa*
no journal, ,
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been in the spotlight due to their unique and interesting properties. It is remarkable that their physicochemical properties are controlled by varying cations and anions. Magnetic IL is an example. The first discovered magnetic IL C mimFeCl
mimFeCl is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (=
is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (= 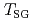 ) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C
) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C mimFeCl
mimFeCl exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below
exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below 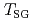 , which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. Since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin cluster.
, which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. Since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin cluster.
Kiyanagi, Ryoji
no journal, ,
SENJU is a single crystal neutron diffractometer at Material and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. SENJU has been in the user operation for more than 7 years and yielded a number of scientific results out of inorganic, small molecular and magnetic materials. The unique features of SENJU include a wide coverage of solid angle realized by 37 2-dimensional detectors and a wide wavelength spectrum of neutrons, leading to very efficient measurements of Bragg reflections in a large Q-space. In addition to this unique characteristics, SENJU can accommodate a variety of sample environment devices such as a magnet and a furnace. Regarding to the data analysis, an in-house made software, STARGazer, is used to process the date measured on SENJU and we are now working to make STARGazer available through the web in order to provide a better experience for users.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Kobayashi, Makoto*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
The ToF back scattering spectrometer, DNA, installed at the BL02 of MLF in J-PARC, is a tool for quasi-elastic and inelastic neutron scattering. DNA is a unique back-scattering spectrometer with a pulse shaping chopper with maximum rotation speed of 300 Hz. After scattered by the measuring sample, neutrons only with 2.08 meV are selected by Si111 analyzer mirrors. High efficiency and high signal-to-noise ratio are achieved to detect weak signals in inelastic energy region by analyzer mirrors coated with a Gd neutron absorber on the rear of a Si wafer. The subjects of DNA are atomic and spin dynamics ranged from pico to nano second order in bio-molecules, softmatters, and solid state materials such as ionic conductors including batteries and strongly-correlated electron system. In this presentation, in addition of specification of DNA spectrometer, grade-up activities including commissioning work of new analyzer mirrors Si311 and so on will be introduced.